Costochondritis: Can Chiropractic Help?
Costochondritis, also called Tietze syndrome, is often misdiagnosed due to the varied symptoms. It involves the ribs and, depending on the area affected, the pain, discomfort, and other symptoms can mislead doctors to underdiagnose or misdiagnose.
Patients may experience pain in the side, back, and chest which means it can mimic several different conditions, including heart attack, gastrointestinal problems, and lung disease. This can lead to anxiety and increased stress. It is also a chronic problem for some people, causing pain that can range from moderate to intense.
What is costochondritis?
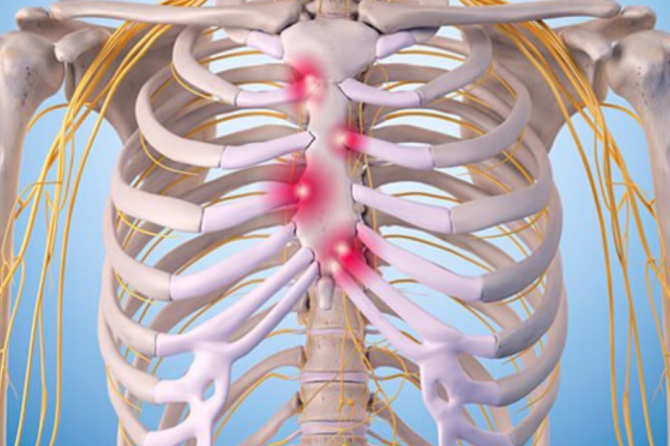
The body is constructed so that the ribs protect the lungs. The first seven pairs connect to the sternum in the front and at two areas in the back along the spine while the lower five pairs are connected in the front by cartilage and in the back along the spine.
Ribs are meant to protect the organs, including the lungs and they are on hinges so that the lungs have room to expand during respiration. Costochondritis occurs when one of those hinges doesn’t work or the cartilage becomes inflamed. The condition is accompanied by pain and sometimes swelling in the affected area.
Symptoms of costochondritis
While swelling may occur in some cases with costochondritis, the primary symptom is pain in the chest area. This pain may become worse when coughing or taking a deep breath and is typically characterized as sharp or aching, although some patients do describe pressure or tightness in the chest area. It often occurs on the left side of the sternum and typically affects several ribs instead of just one. The area is also usually sensitive to touch and pressing on it will increase the pain.
Because the pain occurs in the chest area, many people believe that they are having a heart attack. It is important to note that anyone who experiences chest pain or tightness should seek emergency medical attention immediately in order to rule out heart attack or other life threatening conditions.
How is costochondritis diagnosed?
Usually when a patient seeks treatment for costochondritis, there is no clear cause. However, there are some conditions and activities that have been linked to it and could be the cause or aid in creating the condition. Typical causes of costochondritis include:
- Physical strain such as severe coughing, strenuous exercise, and heavy lifting. People with bronchitis and pneumonia sometimes get costochondritis because of the intense coughing. It is also common among body builders, caused when they strain to lift extremely heavy weights.
- Injury such as getting hit in the chest.
- Joint infection such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi that cause illnesses like aspergillosis, syphilis, and tuberculosis can infect and inflamer the rib joints.
- Arthritis such as ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis have all been linked to costochondritis.
- Tumors including cancerous as well as noncancerous can cause costochondritis. When cancer moves through the body from the lung, thyroid, or breast it can cause inflammation in the rib joints.
People over 40 years old and women are the high-risk categories for costochondritis. Young adults and teenagers are more prone to the connected condition, Tietze syndrome, which is equally frequent in both women and men.
Chiropractic for costochondritis
There is no standard treatment for costochondritis other than managing symptoms. However, chiropractic has proven to be exceptional for managing pain. Chiropractic treatment for the condition involves a gentle approach with anterior thoracic chiropractic adjustments along with treatment for the soft tissue around the affected area and extending along the nerve path.
The chiropractor may also recommend alternating heat and cold directly on the painful areas. Light massage may also work and the chiropractor will show them how to do this at home for continuing self-care. With regular chiropractic treatments and diligent self-care at home, patients can lessen the occurrences of costochondritis and greatly reduce or eliminate the pain.
Leave a reply
Leave a reply