Regaining Spinal Stability after an Accident
Spinal cord injuries can lead to several complications in the human body, even partial to complete paralysis. In fact, some of its disabling conditions include muscular atrophy, chronic pain, infertility, inability to control the bladder and even paralysis of limbs.
So what causes a spinal cord injury? Causes specifically include penetrating injuries due to mechanical disturbance, vertebral fracture or displaced bony fragments which can penetrate the spinal cord or cause segmental spinal nerve injuries. Additional cord insult occurs through subsequent inappropriate manual handling following trauma.
After an accident, it is highly important to immediately rush for medical aid and ensure the spine was not injured. A spinal cord injury is a neurosurgical emergency, as spinal stability is vital to lead a normal, healthy life. A speedy diagnosis and medical attention therefore give patients the highest change to prevent everlasting loss of function.
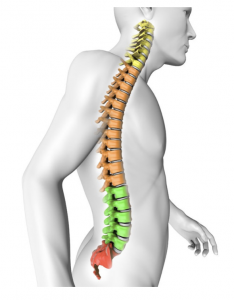
Some Facts about Spinal InjuryThe spinal cord and brain make up the central nervous system. The cord is particularly made up of a group of nerves called tracts. These nerve cells extend downwards from the base of the brain and onto different parts of the body. Messages are then carried through these tracts in the spinal cord between the brain and rest of the body. There are basically two types of tracts:
The ability to feel and move is determined by how complete or incomplete the damage is and at what level the injury occurs. An injury that happens in the neck (cervical spine, made up of 7 vertebrae, subsequently, a damage at C1 to C7) influences trunk, arms, legs and pelvic organs. This is tetraplaegia, likewise called quadraplaegia. Damage can happen in the upper back (thoracic spine, made up of 12 vertebrae connected to the ribs, T1 to T12), the lower back (lumbar spine, L1 to L5) and the base of the spine (sacral zone S1 to S5). Paraplaegia can influence legs, pelvic organs, and trunk. The higher the injury, the greater potential damage. |
Causes and Treatments
Throughout the past fifty years, research has revealed many effective treatments for spinal injuries. Due to these gradual medical advancements, the fatality rate of spinal injuries now remains low. In fact, as a result of this medical progress, doctors offer treatments to not only help patients survive, but also possibly recover a great deal of function after a spinal cord injury. Now, in order to treat a spinal cord injury, doctors combine medication, surgery, and most likely physical therapy.
Overall, a spinal cord injury may be due to either traumatic or non-traumatic causes. Non-traumatic causes occur over time and include cancer, arthritis, blood vessel problems, infection, inflammation and bleeding.
A traumatic spinal cord injury, most likely due to an accident, requires immediate, comprehensive trauma care. This type of treatment is essential for both survival and long-term results. A competent trauma team can do much to minimize the spread of damage from a spinal cord injury. The long-term prognosis thus depends on the nature and location of the injury, as well as the quality of care received.
Trauma Care
In order to do prevent further injury, the medical team will stabilize the person’s blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. They will also put the head and neck in a special brace to avoid unnecessary movements, which causes further injury. With special care, the medics will then load the patient into an ambulance and take them to trauma care.
At the hospital, a team of doctors will work to ensure that the spinal damage does not get worse. They may even sedate the patient to restrict movement while he or she undergoes diagnostic testing for the injury. Testing consists of MRI’s and CT scans, which will determine the extent and severity of the injury.
If the doctors discover a serious injury to the neck of the spinal cord, the patient may suffer respiratory issues. Doctors solve this problem through intubation, i.e. providing oxygen to the lungs through a tube inserted down the throat.
Unfortunately, spinal cord injuries tend to get worse after the initial phase. Blood flow and blood pressure can fall dramatically just after the injury or after a day or so. As blood pressure decreases, the rate of blood flow typically drops, which causes inflammation. Nerve cells near the site of the injury may also start to die. The exact reason for this is still unknown, however, a corticosteroid drug can decrease the extent of the injury spread.
If a corticosteroid drug is needed, doctors may suggest methylprednisolone (Medrol), which begins the recovery of nerve cell damage. The drug additionally reduces inflammation around with injury when given within eight hours of the injury. Like other steroid medication, methylprednisolone does have side effects. As a result, some doctors believe that it is of little benefit to the patient, while others are convinced its benefits significantly outweigh its risks.
Surgical Procedure
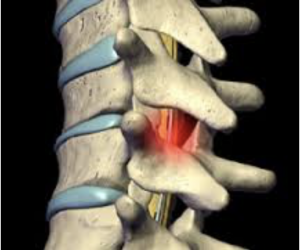
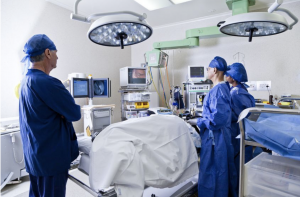
In addition to medication, doctors may suggest surgery to help the patient recover. When an accident causes spinal compression, for example, decompressive surgery will be needed to stabilize the spinal cord. Doctors will then remove bone fragments, foreign objects, herniated disks or fractured vertebrae that are compressing the spine.
The time frame in which it is necessary to perform this emergency surgery is controversial. Some doctors claim that recovery is more likely if surgery is performed as soon after the injury as possible. Other doctors believe the surgery should be performed after several days to ensure the patient’s stability. However, studies show that early intervention is better for the patient. Although additional studies must still be conducted, patients who have undergone surgery within a day of the injury have shown more improvement than those who waited.
Rehabilitation
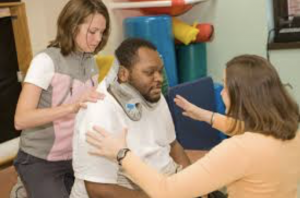
Once the doctors stabilize the patient, it is necessary to begin the rehabilitation process. A variety of specialists, including recreation therapists, occupational therapists, rehabilitation nurses, physical therapists, and rehabilitation psychologists may assist in the recovery process. Typically, the physical therapy stage starts in the hospital. At first, rehab specialists will help the patient regain strength in the legs and arms. Occupational therapists will then help the patient learn new ways of performing routine tasks. Later, if needed, doctors will transfer the patient into a rehabilitation center for additional therapy. The doctor may also permit the patient to receive treatment from his or her home.
Advanced technologies play a vital role in the patient’s recovery. More specifically, new models of wheelchairs, which are lightweight and user-friendly, allow patients to climb stairs without the assistance of others. Some wheelchairs even have the ability to elevate so the patient can easily converse or reach objects at higher levels.
One new technology has become particularly popular amongst patients recovering from spinal cord damage: functional neuromuscular stimulation (FNS). This innovation helps individuals increase their muscle power and even to regain function. It works by invigorating intact peripheral nerves to bring about muscle compressions in incapacitated muscles.
Exercise
Overall, people who suffer from spinal injuries are eager to get back to their normal routines. When a doctor clears the patient for rehab and exercise, it is therefore essential to follow a routine exercise schedule. This will help increase core strength, reduce pain, and reintegrate body movement patterns.
There are three basic principles to remember throughout each exercise and the overall rehabilitation process:
- Breathing is vital not only for life, but also to prevent stress. When a patient begins to feel stressed about recovery, he or she must take three profound deep inhales and exhales.
- Acceptance of the present moment guarantees that the individual does not need to stress about what happened and what will happen. The human body takes time to recover and there is no quick way to re-balance the muscular system. This rule ensures that the patient will steadily progress.
- Awareness is important to motor control and movement patterns. When a person is aware of movement or posture, he/she is more ready to avoid negative behavioral patterns and acknowledge what movements or positions help or obstruct the recuperation procedure.
The patient must always follow the doctor or physical therapist’s instructions. Whether they recommend an exercise or warn not to overdo a movement, it’s important to follow these suggestions closely. For more information about regaining spinal stability after an accident, give us a call! We’re always here to help.
Leave a reply


Leave a reply